This is a personal notes from the course Langchain for LLM application development. This one of the short courses offered by the Deeplearning.
It is mentioned as a 1 hour course, but it took me around 5 hours to complete the course. The course content was using openAI. I tried using Azure OpenAI in all the workbooks, attached the chapter workbook links along with a short excerpt for each chapter.
This course, will give a good introduction to the Langchain and how to use it to build LLM applications using them. Here is the summary of what is being covered in these chapters.
Chapter 1: Models, Prompts and Parsers
- Models refers to the large language models
- Prompts refers to the text that you give to the model. Langchain offers an elegant way to construct these prompts. You can also construct your own prompts.
- Parsers refers to the code that you write to parse the output from the model. Langchain provides conventions, to define the parsers.
Chapter 2: Memory
Memory refers to the ability to store information and retrieve it later. This enables the user to have a chat like conversation with the LLMs.
Some of the memory options discussed in the course are:
-
ConversationBufferMemory - It is the simplest option. Keeps storing all the conversations in the memory and keep sending them in as a context for the subsequent calls. However, this is not a good option because the memory keeps growing and the model will not be able to handle the large memory. Things gets slow and also the cost of the inference will be high.
-
ConversationBufferWindowMemory - It is similar to the
ConversationBufferMemory, but it keeps only the lastnconversations in the memory. This is a better option than theConversationBufferMemory, but still might not be the best. The first conversation of the chat could be very important, and losing that context might have consequences on the conversation. -
ConversationTokenBufferMemory - It is similar to that of
ConversationBufferWindowMemory, but instead of storingnconversations it storesntokens. Still have the same drawback of theConversationBufferWindowMemory. -
ConversationSummaryMemory - Here a summary of the previous conversations are generated and used that as a context for the subsequent calls. This is a better option than the previous ones.
Chapter 3: Chains
Chains are simple wrapper around the Langchain components. It takes the user input, prompts, models and parsers and returns the output. It is a simple wrapper around the Langchain components.
LLMChain - A LLMChain is the most common type of chain. It consists of a PromptTemplate, a model (either an LLM or a ChatModel), and an optional output parser.
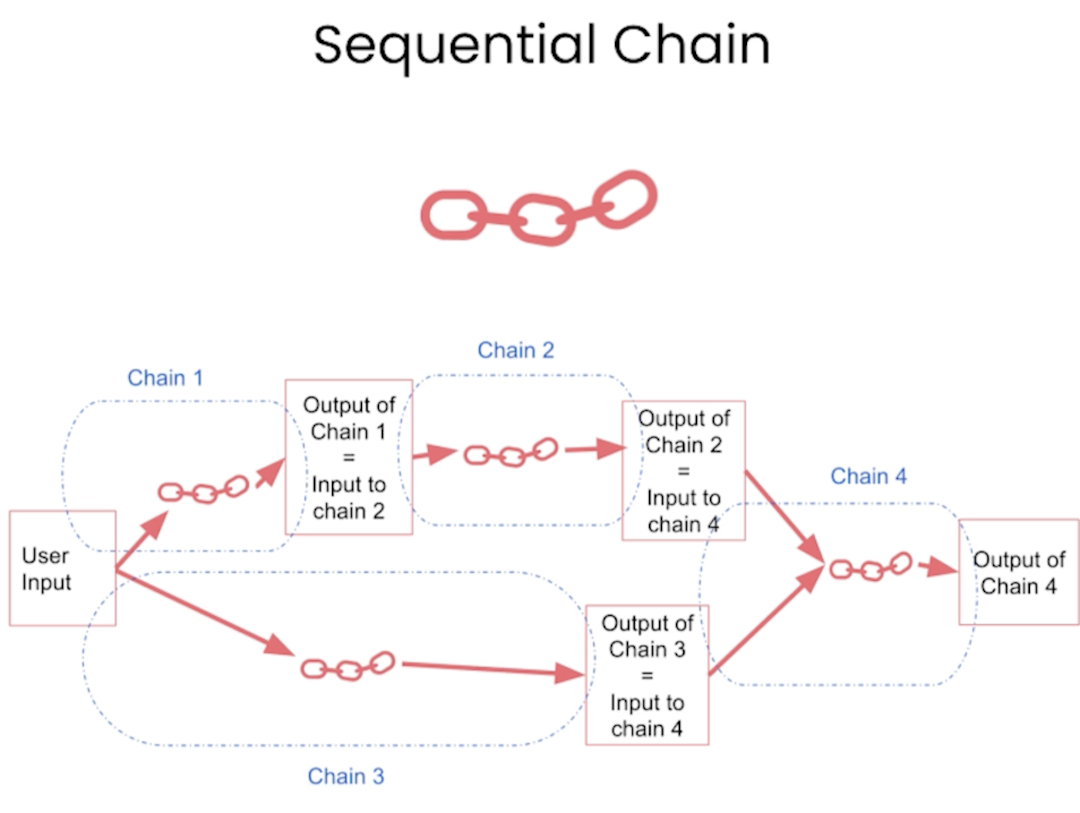
Sequential Chains
Sequential chains allows to chain multiple LLMChain together.
SimpleSequentialChain - this allows the output of the first chain is used as the input for the second chain and so on.
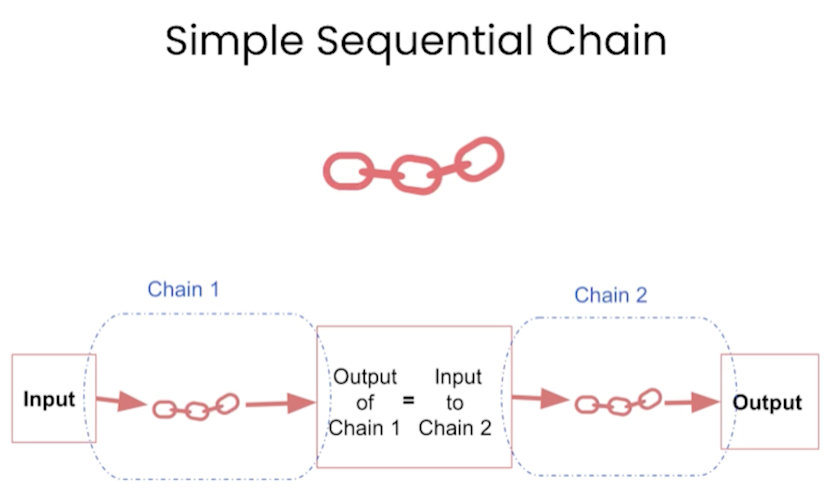
SequentialChain - this allows you to connect multiple LLMChain together and also allows you to connect them (input/output) as you wish.
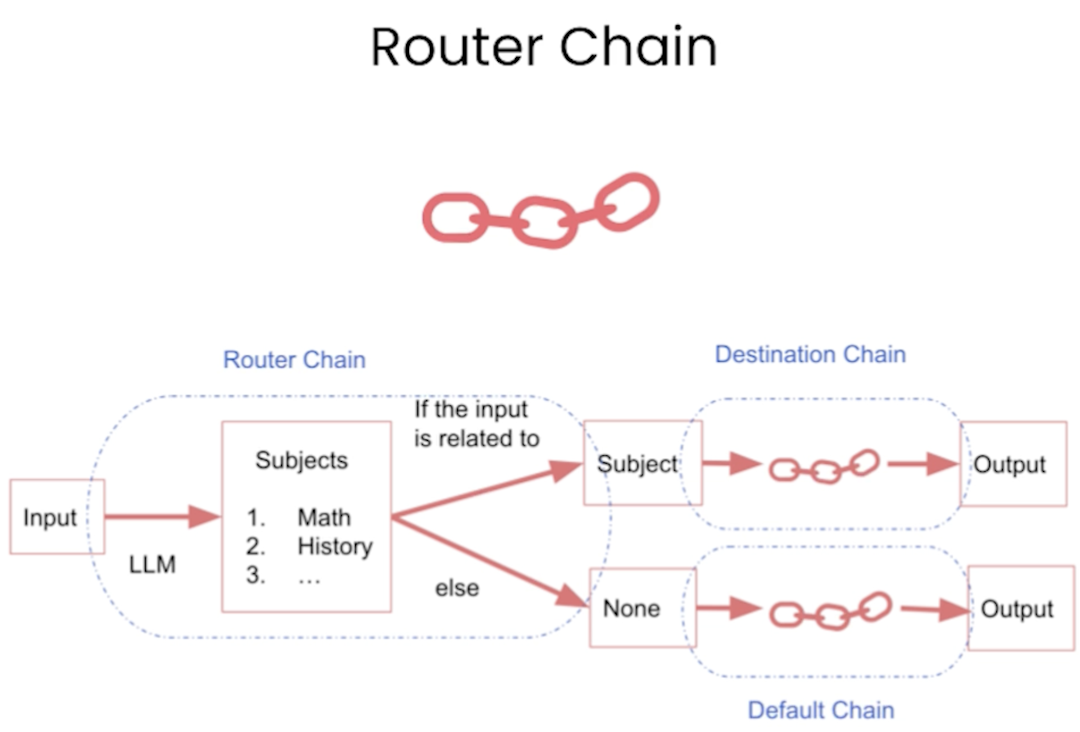
Router Chains
Router chains allows you to map the user input to a specific chain.
Chapter 4: Question and answer
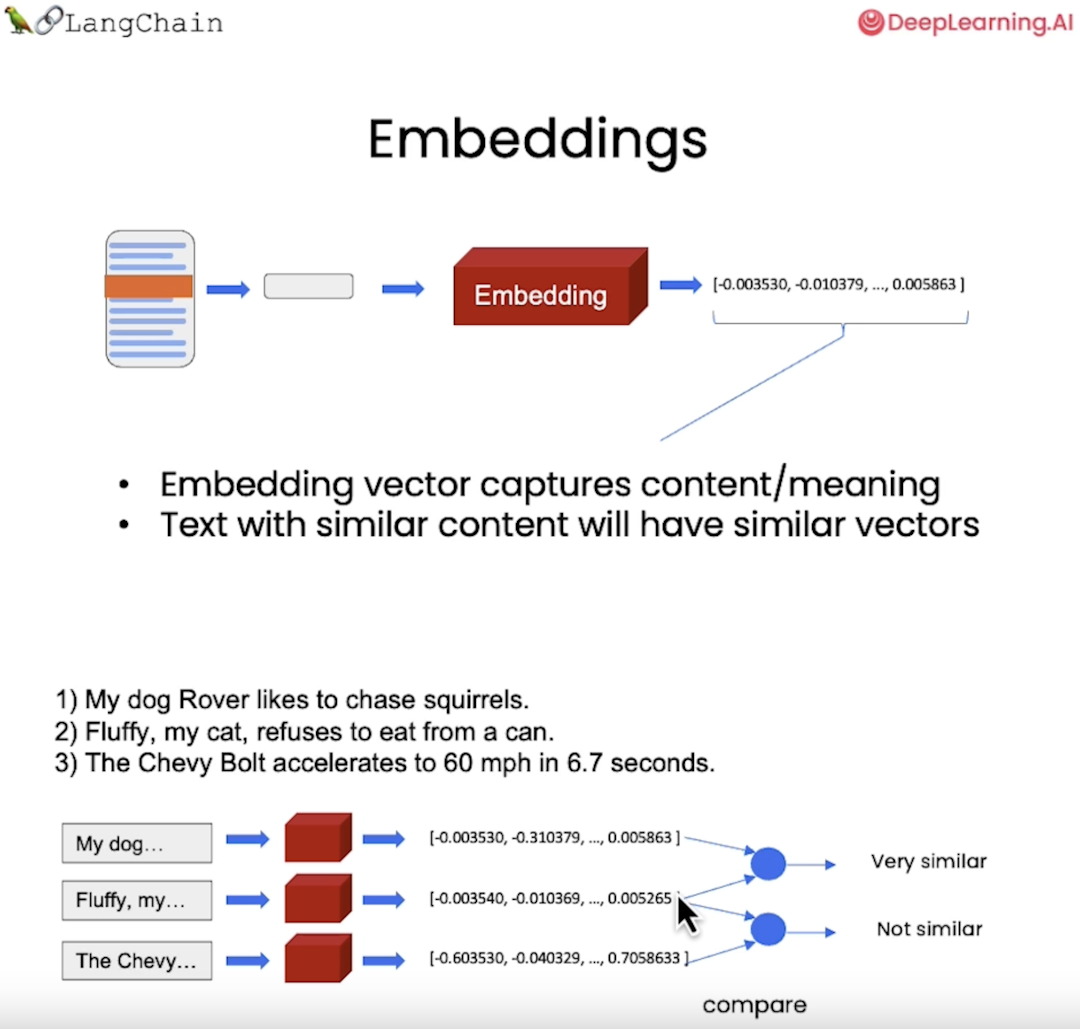
In order to have a Q&A on top of the user's documents. For this to happen, we need to build custom embeddings for the documents.
Langchain provides interfaces to create and interact with the embeddings. My workbook will contain the Azure OpenAI version of these embeddings and the code uses VectorstoreIndexCreator to create the embeddings and DocArrayInMemorySearch to store the embeddings.
Chapter 5: Evaluation
It is possible to perform an evaluation of the LLMs. The evaluation is done by comparing the output of the LLMs with the expected output. Langchain offers interfaces to create these evaluation and perform evaluations.
-
Generate examples for LLMs - This is like creating a test cases for the application under test. Langchain will be able to generate the sample queries and their expected results.
-
Manual evaluation (and debuging) - With the sample queries generated, it is possible to manually evaluate the results and debug the LLMs.
-
LLM-assisted evaluation - Langchain offers
QAEvalChain, which will allow you to evaluate the LLMs. It will take the sample queries and the expected results and build a graded results against the input data.
Chapter 6: Agents
The course discuss only about Zero-Shot ReAct agent. Agent in general are responsible for deciding what step to take next. They can use tools to interact with the world and memory to store information.
-
Built-in toolkit - Langchain offers some built in tools, which can be loaded and the agent can use them to drive the decision making. Example:
-
Building custom tools - Most often, we will need to build tools as a wrapper to our data or APIs, so that the agent can use them. Here you can read about building the custom tools.