Add EditText(s) dynamically and retrieve values - Android
22-March-2011
4 minutes read
android
Adding EditText to your Android application is no different from adding any other form elements except for one thing. Retrieving values from them is slightly different and of course nothing impossible. Just a little more bit of coding and thats it.
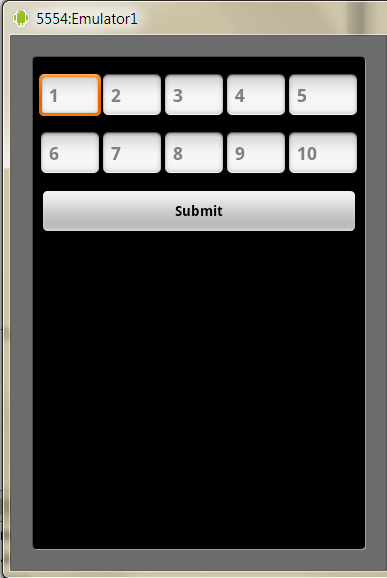
Following code snippet creates a series of EditTexts and also let you to access its values.
import android.app.Activity; import android.os.Bundle; import android.view.View; import android.view.ViewGroup; import android.widget.Button; import android.widget.EditText; import android.widget.LinearLayout; import android.widget.TableLayout; import android.widget.TableRow; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; import static android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams.FILL\_PARENT; import static android.view.ViewGroup.LayoutParams.WRAP\_CONTENT; import static android.widget.LinearLayout.VERTICAL; public class Sample extends Activity { private List<EditText> editTextList = new ArrayList<EditText>(); @Override public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); LinearLayout linearLayout = new LinearLayout(this); ViewGroup.LayoutParams params = new ViewGroup.LayoutParams(FILL\_PARENT, WRAP\_CONTENT); linearLayout.setLayoutParams(params); linearLayout.setOrientation(VERTICAL); int count = 10; linearLayout.addView(tableLayout(count)); linearLayout.addView(submitButton()); setContentView(linearLayout); } private Button submitButton() { Button button = new Button(this); button.setHeight(WRAP\_CONTENT); button.setText("Submit"); button.setOnClickListener(submitListener); return button; } // Access the value of the EditText private View.OnClickListener submitListener = new View.OnClickListener() { public void onClick(View view) { StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder(); for (EditText editText : editTextList) { stringBuilder.append(editText.getText().toString()); } } }; // Using a TableLayout as it provides you with a neat ordering structure private TableLayout tableLayout(int count) { TableLayout tableLayout = new TableLayout(this); tableLayout.setStretchAllColumns(true); int noOfRows = count / 5; for (int i = 0; i < noOfRows; i++) { int rowId = 5 \* i; tableLayout.addView(createOneFullRow(rowId)); } int individualCells = count % 5; tableLayout.addView(createLeftOverCells(individualCells, count)); return tableLayout; } private TableRow createLeftOverCells(int individualCells, int count) { TableRow tableRow = new TableRow(this); tableRow.setPadding(0, 10, 0, 0); int rowId = count - individualCells; for (int i = 1; i <= individualCells; i++) { tableRow.addView(editText(String.valueOf(rowId + i))); } return tableRow; } private TableRow createOneFullRow(int rowId) { TableRow tableRow = new TableRow(this); tableRow.setPadding(0, 10, 0, 0); for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { tableRow.addView(editText(String.valueOf(rowId + i))); } return tableRow; } private EditText editText(String hint) { EditText editText = new EditText(this); editText.setId(Integer.valueOf(hint)); editText.setHint(hint); editTextList.add(editText); return editText; } }